Introduction
The maintenance of a healthy blood sugar level falls under being crucial to health, particularly when one wants to avoid or manage diabetes. Keep your body’s glucose level in check and consider how it varies with age and sex, and lifestyle so that you can actually take care of yourself. Here is a blood sugar level chart that tells you the blood sugar levels; that is, the safe blood sugar range and normal blood sugar level for men and women. Along with this, we reveal an extensive blood sugar level chart by age to enable understanding of how the blood sugar levels change with age. If you are watching your levels for medical purposes or just like to stay informed, this article will be a clear and worthy resource in your journey toward good health.
What is Blood Sugar Level?
Blood sugar level is the concentration of glucose suspended within a person’s blood at a given instant. Glucose is a sugar borne of food, being the principal source of energy for the human body. Taking a meal will also constitute chemical digestion, wherein carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, and this glucose enters the bloodstream. Insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, assists cells in absorbing glucose to be used for energy. If not maintained, high or low sugar levels can lead to serious health complications; hence, maintaining a stable blood sugar level is essential for appropriate body function.
Why Blood Sugar Levels Vary With Age?
As we grow, our body experiences metabolic and hormonal changes that usually change the way glucose is processed by our bodies. Hence, blood sugar differs with age. The following are some major reasons explaining why this occurs:
- Reduction in Insulin Sensitivity: As people grow older, the cells tend to lose their response to coupling with insulin, which raises blood sugar levels, even when insulin production is normal.
- Changes in Level of Exercise: Aging is always accompanied by a decrease in physical activity. The lack of exercise decreases the body’s use of glucose; hence, it releases excess glucose into circulation
- Loss of Muscle Mass: Aging is commonly associated with a natural loss of muscle mass, as muscle cells help in glucose absorption. Decreased muscle mass could contribute to increased blood sugar levels.
- Slower Metabolism: Older adults tend to have a slower metabolism that affects the speed of breaking down food and utilization of glucose, which would in turn keep the glucose levels up for an extended period.
You Can Also Read:- Normal Cholesterol Level Range: Age-Wise Chart & Guide
Blood Sugar Level Chart by Age (Fasting & Post-Meal)
Being knowledgeable about changes in blood sugar levels that come with aging can make it easier for you to assess your health. On the other hand, below is a blood sugar level chart according to age, which lists the approximate fasting and post-prandial range of blood sugar for the different age groups. These values represent what many consider to be the normal blood sugar level for men and women, but this may vary slightly according to individual health conditions.
| Age Group | Fasting Blood Sugar (mg/dL) | Post-Meal Blood Sugar (mg/dL) |
| Children (6–12) | 70 to 100 | Below 140 |
| Teenagers (13–19) | 70 to 105 | Below 140 |
| Adults (20–40) | 70 to 99 | Below 140 |
| Middle Age (41–60) | 70 to 100 | Below 140 |
| Seniors (60+) | 70 to 110 | Below 150 |
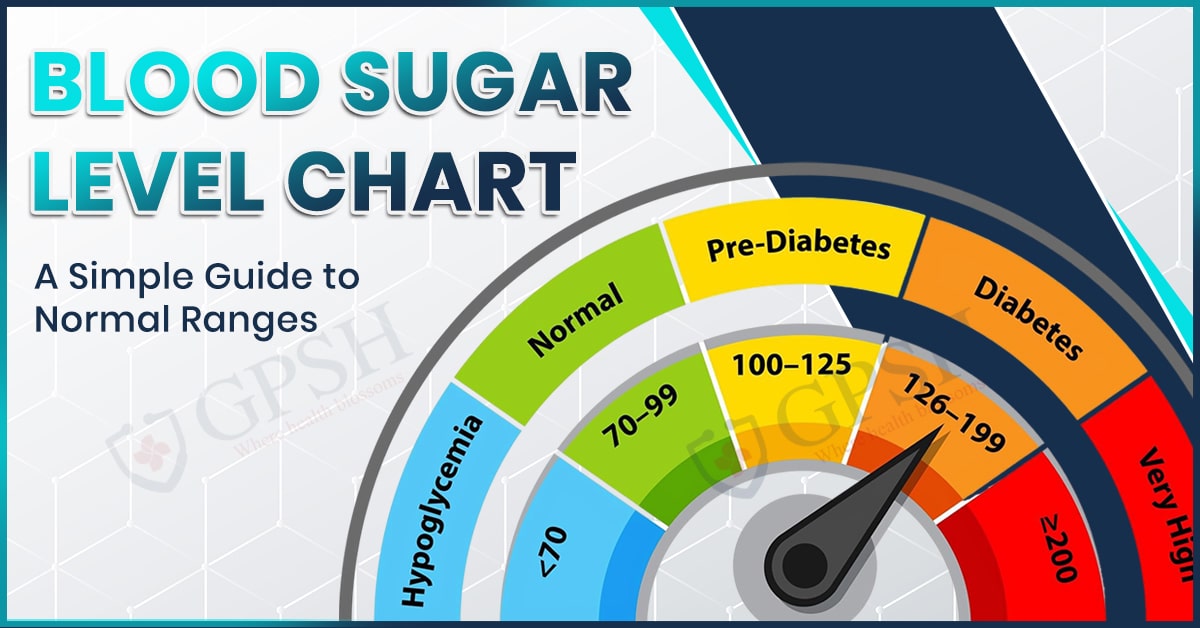
What Is a Normal Blood Sugar Range?
Normal blood sugar ranges are considered healthy levels of glucose in the blood for the body to function well. These levels may vary slightly in respect to the time of day, whether you have eaten in the period, or other individual health factors. In general, as per the medical guidelines, the following ranges fall within a normal state for most healthy individuals:
- Fasting (meaning: before eating): 70 through 99 mg/dL
- Two hours post-meal (post-prandial): Less than 140 mg/dL
- Random blood sugar (taken anytime throughout the day): Less than 140 mg/dL
- Before bedtime: 100 to 140 mg/dL
Symptoms of Abnormal Blood Sugar Levels
When blood sugar passes beyond normal levels, certain signs emerge and are discernible. If recognized early, these signs may help control or avoid complications related to both high or low blood sugar. Some symptoms of abnormal sugar levels are as follows:
Symptoms of High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia)
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Fatigue or weakness
- Blurred vision
- Headaches
- Slow healing of cuts or wounds
- Unexplained weight loss
- Dry mouth or skin
Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
- Shakiness or trembling
- Sudden hunger
- Sweating
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Irritability or mood changes
- Rapid heartbeat
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- Fainting or loss of consciousness in severe cases
You can read also:- Home Remedies to get rid of gas from the stomach instantly?
When Should You Check Blood Sugar Levels?
Knowing the right time of day to check the levels of sugar in the blood is really essential for the proper monitoring of the disease and its management. The time of testing varies according to the treatment aim of an individual, their medication, and whether they are treating type 1 or type 2 diabetes. The common times are:
Fasting (Post-Waking and Pre-Eating): This first check in the morning gives a baseline reading. It is useful in the determination of how well an individual counteracts the rise of glucose levels during sleep. Normal limits range from 70 to 99 mg/dL.
- Before Meals: Pre-meal testing demonstrates the regulators of glucose during the day. Its good levels come in a range of 70 to 130 mg/dL.
- Two Hours After Meals (Post-Meal): Testing at this time tells you about the function of your body with food and how food changes the level of glucose in your blood. The target is less than 140 mg/dL.
- Before Bedtime: A reading at bedtime could inform whether levels are stable overnight and can help to lower the risk of overnight lows or highs. Preferred range between 100 and 140 mg/dL
- During Symptoms of High or Low Blood Sugar: You should check your levels immediately if you happen to feel dizzy, weak, thirsty, or shaky to confirm whether it is a blood sugar spike or drop.
- Before and After Physical Activity: Since activities alter one’s blood sugar, one must test before and after workouts to adjust one’s meals, medicine, or activities accordingly.
How to Maintain Normal Sugar Levels at Any Age
Maintaining normal blood sugar has much to offer regardless of age. Being young, middle-aged, or old, having glucose levels within the limits can save anyone from multiple side effects down the line, keeping them healthy for the most part. Just a few lifestyle choices on your part can efficiently help sustain that level in the normal zone. Some helpful tips to maintain blood sugar levels at any age:
- Eat Well: Include various whole grains, lean protein, healthy fats, and fresh vegetables in your diet. Avoid foods high in added sugar or refined carbohydrates as they cause spikes in blood sugar. Knowing how foods interact with your body and referring to a blood sugar levels chart can guide you.
- Physically Active: Exercise increases the efficiency of insulin and lowers blood glucose levels. For at least 30 minutes, engage in brisk walking, swimming, cycling, etc., for most days of the week.
- Drink a Good Amount of Liquids: Take good amounts of water for better functioning of the kidneys, which allows them to filter out excess sugar through urine, and to support good metabolism.
- Quality Sleep: Quality sleep maintains hormonal balance to control blood sugar and eating. Aim for 7 to 9 hours of uninterrupted sleep nightly to permit the body’s natural glucose regulation.
- Find Ways to Relax: Prolonged stress can increase cortisol levels, a hormone that elevates blood sugar levels. Try relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to keep stress at bay.
- Regular Blood Sugar Checks: Whether you are already managing diabetes or keeping a watchful eye, staying aware helps you take timely action. Check against the blood sugar level chart by age to see if yours falls under the healthy category.
- Medication Compliance: If prescribed medication or insulin by your doctor, take it as directed. You should not miss doses, nor should you alter medication without consulting your doctor, because you risk unbalancing sugar levels.
- Restraining from Smoking and Limiting Alcohol: Smoking tends to inhibit the proper functioning of insulin, whereas large doses of alcohol are disruptive to blood sugar control. Try to avoid these to promote smooth glucose control.
Conclusion
Blood sugar level monitoring is vital for preventing diabetic complications and other metabolic disorders. Once one understands the ideal values by blood sugar levels chart and the normal blood sugar range, one can go further using a reliable blood sugar level chart by age to help ensure they are within healthy limits. Whether you have the management of a disease or are just looking to stay informed, knowing the normal blood sugar level for men and women is certainly one step to general well-being. Accurately diagnosed and treated, Shekhawati Hospital can offer you trusted care and support with your individual needs.