Yoga for a Healthy Heart: Poses and Practices to Boost Cardiovascular Wellness
Introduction
Since today the fast-moving world places so much emphasis on heart health, it is really important that life be kept healthy. Yoga, this age-old art of connecting the human body and mind, promises to be the best way to go about the natural upkeep of cardiac wellness. With selected yoga asanas and yoga poses for a healthy heart, one can enhance blood circulation, curb stress, and build the heart muscle.
We shall look at some of these yoga asanas conducive to a healthy heart during this discussion, along with some peaceful yoga poses, breathing methods, and lifestyle instructions that collectively supply the cardiovascular system with strength and resilience. Regardless of whether you are beginning your training or are deepening it, these practices can easily be integrated into daily life for the long-term benefit of the heart.
Why Yoga is Good for Heart Health
Yoga is an exercise, but it is an all-encompassing art and science of holistic health for the mind and body. Thus, it can be enhanced in cases of heart conditions. These include the following main advantages for the cardiovascular system:
- Yoga reduces stress and anxiety in that it stills the mind and lowers the level of stress hormones within the body. The whole palladium of elevation of blood pressure, which then leads to heart diseases, gives higher resistance.
- Yoga improves circulation, which is the correct flow of blood and adequate supply of oxygen throughout the body, and on the other hand, increases cardiovascular functioning.
- Regular yoga practice also helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels, thereby reducing strain on the heart and arteries.
- Yoga helps improve heart rate variability measure of how well the heart responds to stress and dynamic environments. An increased variability is an indication of a healthy heart.
- Certain yoga postures are good for the heart by gently building upon the heart muscles, as they would in any aerobic type of exercise.
- Yoga can also aid in weight management. A consistent yoga practice supports balanced metabolism and body weight, reducing the risk of heart-related conditions like high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity.
How Yoga Supports Cardiovascular Wellness?
The goods, or the disadvantages, attract this yoga cardiovascular company in that it deals with some of the physical and mental factors that influence the heart. Consequently, yoga exercises create a positive effect on the whole circulatory system with a mixture of movements, breath control, and consciousness.
- Yoga asanas will stimulate the processing of blood circulation, muscle stretching and strengthening, and increase the flexibility of the blood vessels; such loving movements will retain good blood pressure and cholesterol level, both important to heart health.
- Thus comes the pranayama, or the laws of breath in yoga, which regulate your nervous system and provide relaxation. This helps to counteract any harmful stress response in the body that would also put pressure on the heart and result in hypertension.
- The calm mental state brought about by meditation or deep concentration on breathing regulates emotional stability, thus working towards cardiovascular health. Yoga further helps with steady exercise practice and self-care-even more meriting long-term heart health.
- By integrating yoga poses for a healthy heart into your routine, you not only boost your physical fitness but also nurture emotional balance and overall cardiovascular strength.
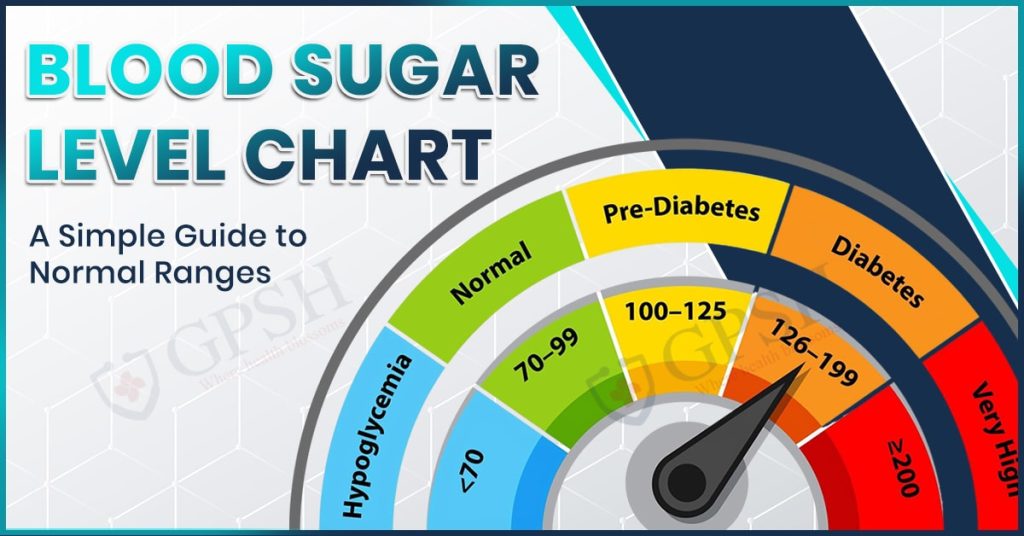
You Can Also Read:- Blood Sugar Level Chart: A Simple Guide to Normal Ranges
Breathing Exercises (Pranayama) for a Stronger Heart
Pranayama, the art of controlled breathing, is a unique process in yoga for balancing and maintaining a healthy functioning heart and for ensuring overall cardiovascular health. This type of breath work activates the parasympathetic nervous system; by dilating the blood vessels, it increases the flow of oxygen and squeezes out cortisol, which sends stress signals to the heart.
Several pranayamas that support heart health include the following:
- Anulom Vilom (Alternate Nostril Breathing): It tries to balance the flow of energy in the body while calming the mind. It lowers blood pressure, enhances circulation, and lessens stress, all of which benefit the heart.
- Bhramari (Bee Breath): Bhramari has calming effects on the brain and nervous system. It reduces heart rate and blood pressure while increasing relaxation and emotional stability.
- Deep Diaphragmatic Breathing: Slow deep breaths taken from the diaphragm increase the intake of oxygen while decreasing the demand on the heart. It helps especially when combined with ailments like high blood pressure or undue anxiety that produce spasms of the heart.
- Sheetali Pranayama (Cooling Breath): The technique basically acts as a cool restorative breath for calming down the mind and relieving stress, together with emotional uplift that benefits the heart.
- Ujjayi Breath (Victorious Breath): This is now the most used and well-liked breath, along with dynamic yoga flows. Its function is lung strengthening and endurance building; physically, it helps to keep the heart strong, and mentally, it gives concentration.
Yoga Poses for a Healthy Heart
Practicing the appropriate yoga poses for heart health will enhance circulation, reduce stress, strengthen the cardiovascular system, and bring about emotional balance. The asanas are very gentle and supportive of heart health with a sincere and consistent practice.
Here are some of the best yoga asanas for a healthy heart:
- Tadasana (Mountain Pose): A basic standing pose that improves posture, allows for stable and deep breathing, and creates a feeling of calm concentration to lessen stress and regulate blood pressure.
- Vrikshasana (Tree Pose): Building balance and concentration, this pose calms the mind and strengthens neuromuscular coordination, ensuring mental and physical stability.
- Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose): Cobra Pose opens the chest, strengthens the back muscles, and increases oxygen intake. With the help of this yoga pose, fatigue and stress, which are harmful to heart health, are relieved.
- Setu Bandhasana (Bridge Pose): This backbend stretches the chest and facilitates blood circulation. It also helps in reducing anxiety and fatigue while strengthening the heart and lungs.
- Viparita Karani (Legs-Up-the-Wall Pose): This thoroughly restorative posture increases blood flow toward the heart, calms the nervous system, and reduces swelling in the legs, making it a stellar pose for cardiovascular support.
- Adho Mukha Svanasana (Downward-Facing Dog): This more restorative pose promotes blood flow to the brain and heart, relieves tension, and strengthens the entire body while placing no burdens on the cardiovascular system.
- Shavasana (Corpse Pose): Usually used at the end of a yoga session, Shavasana is for complete body relaxation. The heart rate drops, blood pressure goes down, and the nervous system resets, creating a healthy environment for the heart.
You Can Also Read:- Home Remedies to get rid of gas from the stomach instantly?
Tips for Practicing Yoga Safely with a Heart Condition
If you are dealing with a heart condition, practicing yoga can be beneficial for your overall wellness routine. Nevertheless, it is essential to approach yoga with caution and awareness. Below are some very important tips you’ll want to consider if you are to safely carry out yoga work while minding your heart:
- Get Your Doctor’s Opinion First: Discuss with your doctor and find out whether you can engage in any form of yoga class, given your particular heart condition and general health status.
- Know Which Styles to Practice: Gentle restorative classes, for example, Hatha yoga, Iyengar yoga, or chair yoga, are best. Unless specifically approved by your doctor for some very particular reasons, stay away from high-intensity classes such as power yoga or hot yoga.
- Go Slowly and Mindfully: Practice basic and uncomplicated yoga exercises to begin with, the ones that do not stress the body. Apply the best technique for the poses and never rush.
- Listen to Your Body’s Signals: Observe in detail how your body reacts during a yoga session and after it. Should you ever feel dizzy, encounter shortness of breath, feel any kind of pain in your chest, or experience unusual imbalance in fatigue, stop immediately and seek medical assistance.
- Do Not Exceed Your Limits: Never force yourself beyond the limits of tolerability. Use blocks, straps, or cushions so you can make any pose safer and easier to hold.
- Gentle Breathing Techniques: Choose calming pranayama techniques like Anulom Vilom or deep belly breathing. Avoid those that are forceful, such as Kapalabhati and Bhastrika, which could be dangerous for persons with cardiac conditions.
- Hydrate Yourself and Inhale Comfortable Atmosphere: Keep yourself well-hydrated and seek a quiet, well-ventilated place to enjoy the exercise in comfort without overhearing.
- Balance Dryly with Consistency: You should remain consistent in its application as the benefits thereof will accrue in due time. However, always maintain balance with a sufficient amount of rest; excess leads to tiredness and stress for the heart.
Conclusion
Yoga is a holistic and natural way of maintaining a healthy heart through physical postures, breathing exercises, and mental relaxation. The smooth flow of yoga and pranayama for a healthy heart eases tension, improves blood circulation, and enhances cardiovascular functioning. Whether it is to keep away from a heart-related problem or to deal with one, yoga practiced mindfully surely makes a good and safe choice to be embedded into everyday life.
Get professional help and some information from Shekhawati Hospital if you want to stay informed about heart health and promote Vedic yoga for a heart-friendly lifestyle. While one aspect of yoga is flexibility, its greater importance is providing a nurturing environment for a healthy, well-balanced life.
Yoga for a Healthy Heart: Poses and Practices to Boost Cardiovascular Wellness Read More »